The United States stands at a pivotal moment in blockchain technology adoption. As both government agencies and enterprises seek innovative solutions to enhance security, transparency, and efficiency, blockchain has emerged as a transformative force. This decentralized ledger technology is moving beyond cryptocurrency applications into core infrastructure for public services, supply chain management, and financial systems. With federal initiatives gaining momentum and enterprise implementation accelerating, understanding the current landscape and future trajectory of blockchain adoption has become essential for organizational strategy and competitive advantage.
Government Adoption of Blockchain Technology
The U.S. government has been strategically exploring blockchain applications across multiple agencies. This technology offers unprecedented opportunities to enhance public service delivery, secure sensitive data, and streamline operations. From digital identity management to supply chain transparency, federal and state agencies are leveraging blockchain’s immutable ledger to build more resilient and efficient systems.
Current Federal Blockchain Initiatives
- The Department of Homeland Security has invested over $9 million in blockchain startups through its Silicon Valley Innovation Program, focusing on digital credentials and supply chain security.
- The U.S. Food and Drug Administration launched the DSCSA Blockchain Interoperability Pilot to enhance pharmaceutical supply chain tracking and prevent counterfeit medications.
- The General Services Administration implemented a blockchain-based system for automating vendor verification in federal procurement processes.
- The Department of Health and Human Services uses blockchain for healthcare data management and sharing while maintaining HIPAA compliance.
Case Study: Digital Dollar Project
The Federal Reserve, in collaboration with the Digital Dollar Foundation, has been researching Central Bank Digital Currency (CBDC) implementation. This initiative explores how blockchain could support a digital version of the U.S. dollar, potentially revolutionizing payment systems while maintaining monetary policy control. The project has completed multiple technical experiments and published findings on security models, privacy considerations, and interoperability with existing financial infrastructure.
State-Level Blockchain Adoption
Beyond federal initiatives, individual states have become blockchain innovation hubs:
Wyoming
Established the most progressive blockchain legislation in the country, creating a regulatory framework for digital assets and recognizing DAOs (Decentralized Autonomous Organizations) as legal entities.
Colorado
Implemented blockchain for government record management and became the first state to accept cryptocurrency for tax payments through a blockchain-based system.
Regulatory Challenges
Progress
- Executive Order on Ensuring Responsible Development of Digital Assets providing a framework for regulation
- SEC guidance on token classification and securities laws
- State-level regulatory sandboxes allowing controlled innovation
Challenges
- Fragmented regulatory landscape across federal agencies
- Uncertainty around jurisdiction and enforcement
- Balancing innovation with consumer protection
- Privacy concerns with government blockchain implementations
Navigate the Blockchain Regulatory Landscape
Download our comprehensive guide on blockchain compliance for government and enterprise applications. Stay ahead of regulatory developments and implementation best practices.
Enterprise Blockchain Adoption in the USA

American enterprises across industries are increasingly implementing blockchain solutions to enhance operations, reduce costs, and create new business models. According to Deloitte’s Global Blockchain Survey, 81% of U.S. executives now consider blockchain a mainstream technology, with implementation rates doubling since 2020.
Industry-Specific Blockchain Applications
Financial Services

- JPMorgan’s Onyx platform processes over $1 billion daily in wholesale payments using blockchain
- Goldman Sachs and Digital Asset Holdings created a blockchain-based trading platform for bonds
- Visa’s B2B Connect uses blockchain for cross-border corporate payments
Healthcare

- Humana, MultiPlan, and UnitedHealth Group implemented a blockchain solution for provider data management
- Pfizer uses blockchain for tracking pharmaceutical supply chains
- Change Healthcare processes 30 million transactions daily on its blockchain network
Supply Chain

- Walmart tracks over 25 food products using IBM’s Food Trust blockchain platform
- FedEx implemented blockchain for dispute resolution and customs documentation
- Maersk’s TradeLens platform processes 10 million shipping events weekly
Case Study: Walmart’s Food Traceability Initiative
Walmart’s implementation of blockchain for food safety demonstrates the technology’s transformative potential in supply chain management. By requiring suppliers to input data into IBM’s Food Trust blockchain, Walmart reduced the time needed to trace food from farm to store from 7 days to 2.2 seconds. This implementation has improved recall management, reduced food waste, and enhanced consumer trust. The system now tracks millions of food packages across thousands of suppliers, creating unprecedented supply chain visibility.
ROI and Efficiency Gains
| Benefit Category | Average Improvement | Implementation Timeline | Primary Industries |
| Transaction Processing Costs | 30-40% reduction | 6-12 months | Banking, Insurance, Healthcare |
| Supply Chain Transparency | 65-80% improvement | 12-18 months | Retail, Manufacturing, Pharmaceuticals |
| Document Processing Time | 70-90% reduction | 3-9 months | Legal, Real Estate, Government |
| Fraud Reduction | 40-50% decrease | 9-15 months | Finance, Insurance, Healthcare |
Benefits and Challenges of Blockchain Adoption
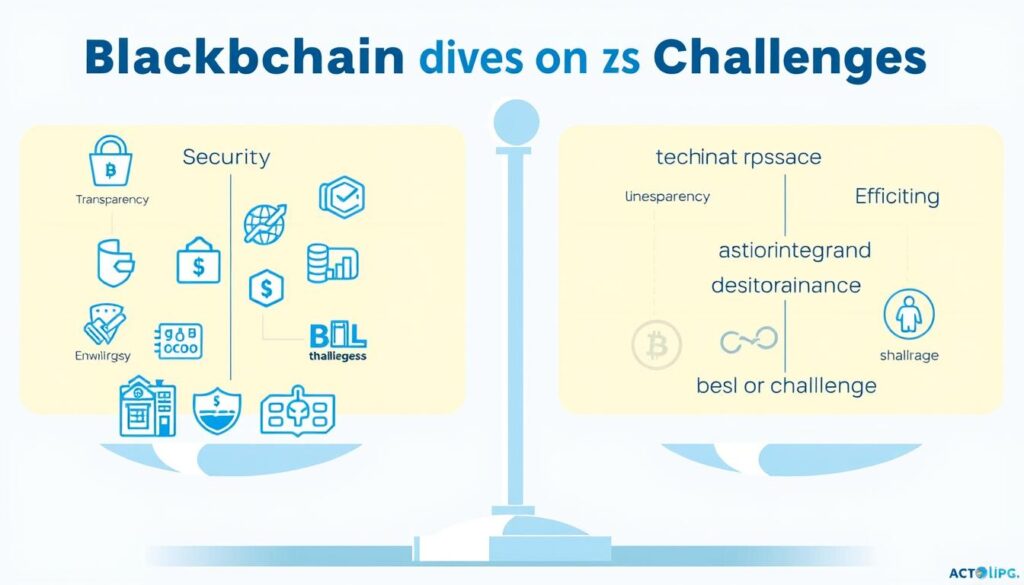
Key Benefits
Enhanced Security
Blockchain’s cryptographic foundation provides tamper-proof records and enhanced protection against cyber threats. Government agencies handling sensitive citizen data and enterprises managing proprietary information benefit from blockchain’s immutable audit trails and distributed architecture, which eliminates single points of failure.
Increased Transparency
The technology enables unprecedented visibility into transactions and processes. Public sector applications include transparent procurement systems and traceable fund allocation, while enterprises leverage blockchain for supply chain visibility and stakeholder reporting.
Operational Efficiency
Smart contracts automate processes that traditionally required intermediaries, reducing administrative overhead and accelerating transactions. Government agencies have reduced paperwork processing times by up to 90%, while enterprises report 30-50% efficiency gains in contract execution.
Implementation Challenges

Scalability Limitations
Many blockchain networks face throughput constraints that limit transaction processing capacity. Enterprise implementations often require thousands of transactions per second, which exceeds the capabilities of many public blockchains. Organizations are addressing this through layer-2 solutions, sidechains, and optimized consensus mechanisms that balance security with performance.
Interoperability Challenges
The proliferation of blockchain platforms has created silos that limit cross-chain communication. Government agencies and enterprises with complex ecosystems need solutions that can operate across multiple blockchain networks. Projects like Polkadot, Cosmos, and the Interwork Alliance are developing standards and protocols to enable seamless data exchange between different blockchain systems.
Energy Consumption Concerns
Proof-of-Work blockchains consume significant energy, raising sustainability concerns. Organizations with environmental commitments are increasingly adopting Proof-of-Stake and other energy-efficient consensus mechanisms. The transition to greener blockchain infrastructure aligns with corporate sustainability goals and government environmental policies.
Legacy System Integration
Connecting blockchain solutions with existing enterprise systems presents technical challenges. Organizations are developing middleware and API layers to bridge blockchain networks with legacy databases and software. Successful implementations typically follow a phased approach, gradually migrating processes to blockchain while maintaining operational continuity.
Future Outlook: Blockchain in USA 2025-2030
The next five years will see blockchain technology in USA government and enterprise sectors evolve from experimental projects to mission-critical infrastructure. Several converging trends will shape this transformation:
AI-Blockchain Convergence
The integration of artificial intelligence with blockchain networks will create powerful new capabilities for both government and enterprise applications:
- AI-powered smart contracts that can adapt to changing conditions and optimize execution parameters
- Enhanced fraud detection through machine learning algorithms analyzing blockchain transaction patterns
- Automated compliance monitoring for regulatory requirements across complex blockchain networks
- Predictive analytics for supply chain optimization based on blockchain-verified data

Regulatory Maturation
The regulatory landscape for blockchain technology will continue to evolve, with several anticipated developments:
- Comprehensive federal framework for digital assets and blockchain applications by 2026
- Standardized compliance protocols for government blockchain implementations
- International coordination on blockchain standards and cross-border applications
- Industry-specific regulatory guidance for healthcare, finance, and critical infrastructure
Enterprise Blockchain Ecosystems
By 2030, enterprise blockchain adoption will shift from isolated use cases to interconnected ecosystems:
- Industry-wide blockchain consortia managing shared infrastructure for entire sectors
- Seamless integration between public and private blockchains for different business functions
- Blockchain-as-a-Service offerings becoming standard components of enterprise IT stacks
- Tokenization of traditional assets creating new markets and business models
Government Digital Infrastructure
Public sector blockchain adoption will accelerate as part of broader digital transformation initiatives:
- Digital identity frameworks based on blockchain for secure citizen services
- Interagency blockchain networks streamlining government operations
- Blockchain-based voting systems piloted in local and state elections
- Public-private blockchain partnerships for critical infrastructure security
Strategic Recommendations for Stakeholders
For Government Agencies
- Develop blockchain literacy programs for government personnel
- Create regulatory sandboxes to test blockchain applications safely
- Establish cross-agency working groups to coordinate blockchain initiatives
- Prioritize use cases with clear ROI and citizen benefit
For Enterprises
- Conduct blockchain readiness assessments to identify high-value opportunities
- Start with focused pilot projects before scaling to enterprise-wide implementation
- Join industry consortia to share development costs and establish standards
- Develop talent acquisition strategies for blockchain expertise
For Technology Providers
- Focus on interoperability solutions that connect different blockchain networks
- Develop industry-specific blockchain templates to accelerate implementation
- Create user-friendly interfaces that abstract blockchain complexity
- Build compliance tools that automate regulatory requirements

Implementation Roadmap: Organizations should approach blockchain adoption through a phased strategy: (1) Education and assessment, (2) Use case prioritization, (3) Pilot implementation, (4) Evaluation and refinement, and (5) Scaled deployment. This methodical approach minimizes risk while maximizing the potential for successful integration.
Ready to Implement Blockchain in Your Organization?
Our blockchain experts can help you navigate the complexities of implementation, regulatory compliance, and technology selection. Schedule a free consultation to discuss your specific needs and opportunities.
Conclusion
Blockchain technology in USA government and enterprise adoption represents a fundamental shift in how organizations manage data, execute transactions, and build trust. As implementation accelerates across public and private sectors, the technology is moving beyond experimental use cases to become essential infrastructure for digital operations. Organizations that develop clear blockchain strategies now will be positioned to capture significant competitive advantages in efficiency, security, and innovation.
The convergence of blockchain with other emerging technologies like AI, IoT, and advanced analytics will unlock even greater potential in the coming years. By addressing current challenges in scalability, interoperability, and regulatory compliance, blockchain implementations will continue to mature and deliver increasing value. For both government agencies and enterprises, the question is no longer whether to adopt blockchain, but how to implement it effectively to achieve strategic objectives.


No comments yet