The cryptocurrency market presents unique opportunities for traders who can identify and act on price discrepancies across exchanges. While traditional arbitrage trading has existed for decades, the lightning-fast pace of crypto markets makes manual execution nearly impossible. This is where artificial intelligence transforms the game. AI cryptocurrency arbitrage trading leverages advanced algorithms to detect, analyze, and execute trades in milliseconds—capturing profits that would otherwise be missed by human traders.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll walk through everything you need to know to implement AI-powered arbitrage strategies: from understanding the fundamental concepts to setting up your own automated trading system. Whether you’re a developer looking to build your own solution or a trader seeking to leverage existing tools, you’ll find actionable insights to help you capitalize on cross-exchange price inefficiencies with unprecedented speed and precision.
Understanding Cryptocurrency Arbitrage and Why AI Matters
Crypto arbitrage is a trading strategy that capitalizes on price differences of the same digital asset across different exchanges. For example, if Bitcoin is trading at $65,000 on Binance but $65,300 on Coinbase, a trader could potentially make a $300 profit per Bitcoin (minus fees) by buying on the first exchange and selling on the second.
These price discrepancies exist due to several factors:
- Market fragmentation across dozens of exchanges
- Varying liquidity levels between platforms
- Regional demand differences (like the “Kimchi premium” in South Korea)
- Temporary supply/demand imbalances
- Different trading pair combinations
Why Manual Arbitrage Is Nearly Impossible
While arbitrage opportunities exist, capturing them manually presents significant challenges:
Arbitrage Opportunities
- Price gaps between exchanges can range from 0.5% to 5%+
- Multiple types of arbitrage exist (spatial, triangular, statistical)
- 24/7 market operation creates constant opportunities
Manual Trading Limitations
- Price gaps close within seconds or milliseconds
- Human reaction time is too slow (250-300ms minimum)
- Monitoring multiple exchanges simultaneously is impractical
- Complex calculations needed for fee optimization
How AI Transforms Arbitrage Trading
This is where artificial intelligence creates a competitive advantage. AI cryptocurrency arbitrage trading systems can:
- Monitor dozens of exchanges and thousands of trading pairs simultaneously
- Detect price discrepancies in milliseconds
- Calculate profitability after accounting for fees and slippage
- Execute trades across multiple platforms with minimal latency
- Learn and adapt to changing market conditions
The difference between AI-powered and manual arbitrage is stark. While a human trader might identify and execute one or two opportunities per day, an AI system can potentially capture hundreds, each generating small but consistent profits that compound over time.
| Aspect | Manual Arbitrage | AI-Powered Arbitrage |
| Monitoring Capacity | 2-3 exchanges at once | Unlimited exchanges simultaneously |
| Reaction Time | Seconds (250ms+ human reaction) | Milliseconds (as low as 10ms) |
| Calculation Speed | Slow, error-prone | Instant, precise |
| 24/7 Operation | Impossible | Continuous |
| Adaptability | Limited by human learning | Machine learning improves over time |
| Success Rate | ~5-15% | ~40-80% |
Technical Requirements for AI Cryptocurrency Arbitrage
Before diving into implementation, you’ll need to set up the right infrastructure and tools. Here’s what you’ll need to get started with AI cryptocurrency arbitrage trading:
Essential Tools and Platforms
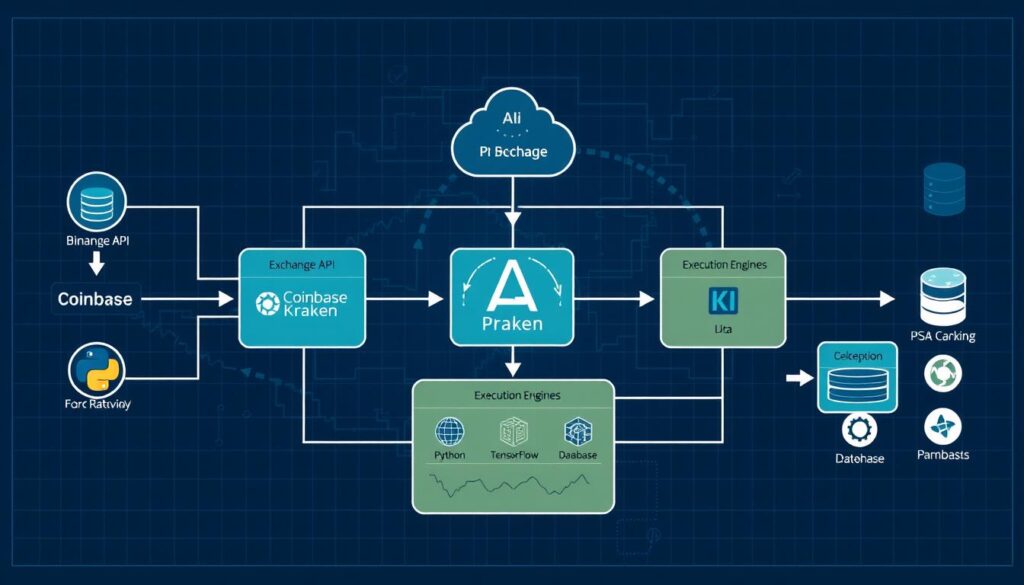
Exchange Accounts
You’ll need accounts on multiple exchanges with API access enabled. Popular options include:
- Binance
- Coinbase Pro
- Kraken
- KuCoin
- Bybit
Development Tools
For building custom AI solutions:
- Python (primary language for AI/ML)
- TensorFlow or PyTorch (ML frameworks)
- Pandas (data manipulation)
- NumPy (numerical computing)
- CCXT library (exchange API wrapper)
Infrastructure
For optimal performance:
- Low-latency server (ideally co-located near exchanges)
- High-speed internet connection
- Database for market data storage
- Monitoring and alerting system
- Backup power and connectivity
Connecting to Exchange APIs
The foundation of any AI arbitrage system is reliable connectivity to exchange APIs. Here’s a Python example using the CCXT library to connect to multiple exchanges:
import ccxt
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
import time
# Initialize exchange objects
binance = ccxt.binance({
'apiKey': 'YOUR_BINANCE_API_KEY',
'secret': 'YOUR_BINANCE_SECRET_KEY',
'enableRateLimit': True
})
coinbase = ccxt.coinbasepro({
'apiKey': 'YOUR_COINBASE_API_KEY',
'secret': 'YOUR_COINBASE_SECRET_KEY',
'password': 'YOUR_COINBASE_API_PASSPHRASE',
'enableRateLimit': True
})
kraken = ccxt.kraken({
'apiKey': 'YOUR_KRAKEN_API_KEY',
'secret': 'YOUR_KRAKEN_SECRET_KEY',
'enableRateLimit': True
})
# Function to fetch order books from multiple exchanges
def fetch_order_books(symbol):
orderbooks = {}
try:
orderbooks['binance'] = binance.fetch_order_book(symbol)
orderbooks['coinbase'] = coinbase.fetch_order_book(symbol)
orderbooks['kraken'] = kraken.fetch_order_book(symbol)
except Exception as e:
print(f"Error fetching orderbooks: {e}")
return orderbooks
# Example usage
btc_usdt_books = fetch_order_books('BTC/USDT')
print(f"Binance best ask: {btc_usdt_books['binance']['asks'][0][0]}")
print(f"Coinbase best ask: {btc_usdt_books['coinbase']['asks'][0][0]}")
print(f"Kraken best ask: {btc_usdt_books['kraken']['asks'][0][0]}")
Ready to Start Building Your AI Arbitrage System?
Download our complete Python code template with pre-configured exchange connections, data processing functions, and basic arbitrage detection algorithms.
Data Requirements
Effective AI cryptocurrency arbitrage trading requires access to high-quality, real-time data:
- Order book data: Depth of market information showing available buy/sell orders
- Trade history: Recent transactions to understand market flow
- Fee structures: Current trading and withdrawal fees for each exchange
- Network confirmation times: For cross-exchange transfers
- Historical arbitrage opportunities: For training machine learning models
The quality and speed of your data feeds will directly impact your arbitrage success rate. Consider using websocket connections for real-time updates rather than RESTful API polling when possible.
AI Strategies for Cryptocurrency Arbitrage

AI brings several powerful capabilities to cryptocurrency arbitrage trading. Let’s explore the key strategies and how they can be implemented:
Real-Time Price Discrepancy Detection
The core of AI cryptocurrency arbitrage trading is the ability to identify price differences across exchanges with minimal latency. Advanced systems use several techniques:
Traditional Algorithmic Approach
The simplest implementation involves continuously polling order books and comparing prices:
def find_arbitrage_opportunities(symbol, min_profit_percent=0.5):
opportunities = []
# Fetch current order books
books = fetch_order_books(symbol)
# Get best prices from each exchange
best_asks = {
'binance': books['binance']['asks'][0][0],
'coinbase': books['coinbase']['asks'][0][0],
'kraken': books['kraken']['asks'][0][0]
}
best_bids = {
'binance': books['binance']['bids'][0][0],
'coinbase': books['coinbase']['bids'][0][0],
'kraken': books['kraken']['bids'][0][0]
}
# Find opportunities
for buy_exchange, ask_price in best_asks.items():
for sell_exchange, bid_price in best_bids.items():
if buy_exchange != sell_exchange:
profit_percent = (bid_price - ask_price) / ask_price * 100
if profit_percent > min_profit_percent:
opportunities.append({
'buy_exchange': buy_exchange,
'sell_exchange': sell_exchange,
'buy_price': ask_price,
'sell_price': bid_price,
'profit_percent': profit_percent
})
return opportunities
Machine Learning Enhancement
AI systems improve on this by adding predictive capabilities:
- Price movement prediction: Forecasting how long a price gap will remain open
- Volume analysis: Determining maximum profitable trade size
- Pattern recognition: Identifying recurring arbitrage opportunities
- Exchange behavior modeling: Learning which exchanges typically lead price movements
- Anomaly detection: Identifying unusual price movements that might indicate arbitrage potential
Risk Management with Predictive Analytics
AI excels at managing the various risks associated with crypto arbitrage:
- Slippage prediction: ML models can estimate potential slippage based on order book depth and historical trade data
- Fee optimization: AI can calculate the most cost-effective execution path considering all fees
- Execution risk assessment: Predicting the probability of successful execution before committing capital
- Market impact modeling: Estimating how your own trades might affect the market
- Volatility forecasting: Adjusting strategies during high-volatility periods
Here’s an example of how a machine learning model might predict slippage for a given trade size:
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestRegressor
# Features for slippage prediction
def extract_orderbook_features(orderbook, trade_size):
features = {}
# Calculate order book depth
depth_5pct = sum([order[1] for order in orderbook['asks'] if order[0] 0 else 1
return features
# Train slippage prediction model (in practice, you'd use historical data)
def train_slippage_model(historical_trades, historical_orderbooks):
features = []
slippage_values = []
for trade, orderbook in zip(historical_trades, historical_orderbooks):
features.append(extract_orderbook_features(orderbook, trade['amount']))
slippage_values.append(trade['slippage_percent'])
model = RandomForestRegressor(n_estimators=100)
model.fit(features, slippage_values)
return model
# Predict slippage for a potential trade
def predict_slippage(model, orderbook, trade_size):
features = extract_orderbook_features(orderbook, trade_size)
predicted_slippage = model.predict([features])[0]
return predicted_slippage
Types of AI Arbitrage Strategies
Spatial Arbitrage
The most straightforward approach: buy on one exchange and sell on another where the price is higher.
AI enhancement: Machine learning models predict which exchange pairs consistently offer profitable opportunities and optimize execution timing.
Triangular Arbitrage
Converting between three different currencies in a circular fashion to profit from pricing inefficiencies (e.g., BTC → ETH → USDT → BTC).
AI enhancement: Neural networks can identify complex multi-step opportunities across dozens of trading pairs simultaneously.
Statistical Arbitrage
Exploiting temporary deviations from historical price relationships between correlated assets.
AI enhancement: Deep learning models can discover non-obvious correlations and predict mean reversion timing with greater accuracy.
Supercharge Your Trading with AI Models
Access our pre-trained machine learning models for slippage prediction, opportunity detection, and risk assessment. Compatible with popular Python ML frameworks.
Step-by-Step Implementation Process
Now that we understand the concepts and tools, let’s walk through the process of building and deploying an AI cryptocurrency arbitrage trading system:
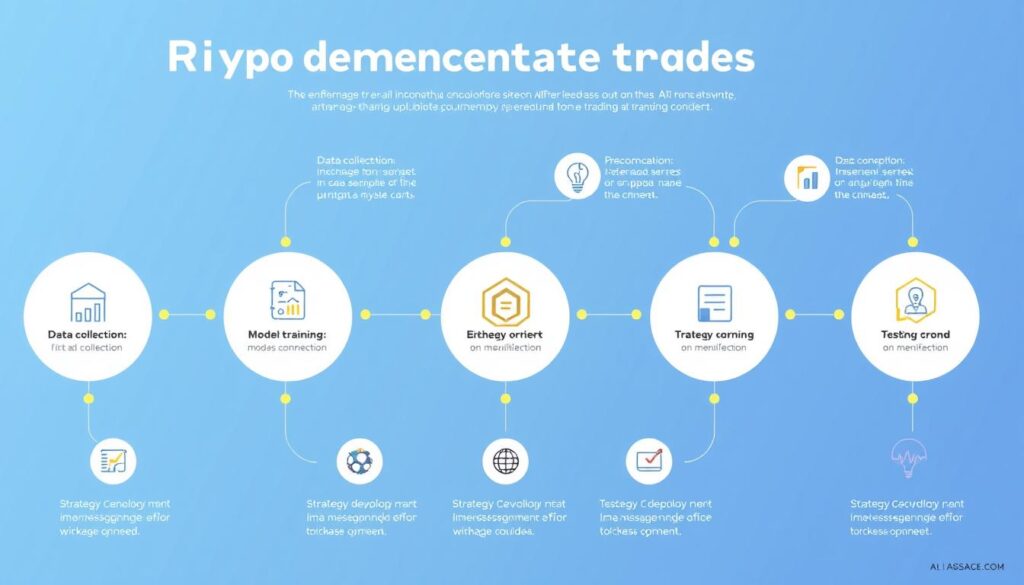
Step 1: Data Collection and Preparation
The foundation of any AI system is high-quality data:
- Set up data collection infrastructure to gather real-time and historical price data from all target exchanges
- Implement websocket connections for minimal latency (example below)
- Create a database schema to store order book snapshots, completed trades, and identified opportunities
- Develop data cleaning pipelines to handle missing values, outliers, and inconsistent timestamps
- Implement feature engineering to extract relevant indicators for your ML models
# Example of websocket connection to Binance
import websocket
import json
import threading
def on_message(ws, message):
data = json.loads(message)
# Process the real-time data
print(f"Received data: {data}")
def on_error(ws, error):
print(f"Error: {error}")
def on_close(ws, close_status_code, close_msg):
print("Connection closed")
def on_open(ws):
print("Connection opened")
# Subscribe to BTC/USDT order book updates
subscribe_msg = {
"method": "SUBSCRIBE",
"params": ["btcusdt@depth"],
"id": 1
}
ws.send(json.dumps(subscribe_msg))
def connect_binance_websocket():
websocket_url = "wss://stream.binance.com:9443/ws"
ws = websocket.WebSocketApp(
websocket_url,
on_open=on_open,
on_message=on_message,
on_error=on_error,
on_close=on_close
)
wst = threading.Thread(target=ws.run_forever)
wst.daemon = True
wst.start()
return ws
# Connect to Binance websocket
binance_ws = connect_binance_websocket()
Step 2: Setting Up AI Algorithms
Next, develop the AI components that will power your arbitrage system:
- Choose appropriate ML frameworks (TensorFlow or PyTorch for deep learning, scikit-learn for traditional ML)
- Design model architecture based on your specific strategy (CNN for pattern recognition, LSTM for time-series prediction)
- Train models on historical data to identify profitable opportunities
- Implement feature normalization to ensure consistent model performance
- Set up validation procedures to prevent overfitting
Here’s a simplified example of a price prediction model using LSTM:
import numpy as np
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.keras.models import Sequential
from tensorflow.keras.layers import LSTM, Dense, Dropout
# Prepare sequence data for LSTM
def create_sequences(data, seq_length):
xs, ys = [], []
for i in range(len(data) - seq_length - 1):
x = data[i:(i + seq_length)]
y = data[i + seq_length]
xs.append(x)
ys.append(y)
return np.array(xs), np.array(ys)
# Build LSTM model for price movement prediction
def build_price_prediction_model(seq_length, features):
model = Sequential()
model.add(LSTM(50, return_sequences=True, input_shape=(seq_length, features)))
model.add(Dropout(0.2))
model.add(LSTM(50, return_sequences=False))
model.add(Dropout(0.2))
model.add(Dense(1))
model.compile(optimizer='adam', loss='mean_squared_error')
return model
# Example usage
seq_length = 60 # Use 60 time steps of data
features = 5 # Number of features per time step
# Create and train model (in practice, you'd use real market data)
X_train, y_train = create_sequences(historical_data, seq_length)
model = build_price_prediction_model(seq_length, features)
model.fit(X_train, y_train, epochs=50, batch_size=32, validation_split=0.1)
# Save the trained model
model.save('price_prediction_model.h5')
Step 3: Executing Cross-Exchange Trades
With data collection and AI models in place, implement the execution engine:
- Develop order execution functions for each exchange
- Implement concurrent execution to minimize time between trades
- Create a transaction manager to track the status of all trades
- Build error handling and retry logic for failed trades
- Implement position reconciliation to ensure balances are accurately tracked
import asyncio
import time
async def execute_arbitrage(opportunity):
"""Execute a cross-exchange arbitrage opportunity"""
# Extract details
buy_exchange_name = opportunity['buy_exchange']
sell_exchange_name = opportunity['sell_exchange']
symbol = opportunity['symbol']
amount = opportunity['amount']
# Get exchange objects
buy_exchange = exchanges[buy_exchange_name]
sell_exchange = exchanges[sell_exchange_name]
# Execute trades concurrently
try:
# Create tasks for concurrent execution
buy_task = asyncio.create_task(
place_order(buy_exchange, symbol, 'buy', amount, opportunity['buy_price'])
)
sell_task = asyncio.create_task(
place_order(sell_exchange, symbol, 'sell', amount, opportunity['sell_price'])
)
# Wait for both orders to complete
buy_result, sell_result = await asyncio.gather(buy_task, sell_task)
# Record the results
trade_id = int(time.time() * 1000)
trade_record = {
'id': trade_id,
'timestamp': time.time(),
'buy_order': buy_result,
'sell_order': sell_result,
'expected_profit': opportunity['expected_profit'],
'status': 'completed'
}
# Store in database
db.trades.insert_one(trade_record)
return trade_record
except Exception as e:
print(f"Error executing arbitrage: {e}")
# Implement error handling and recovery here
return {'status': 'failed', 'error': str(e)}
async def place_order(exchange, symbol, side, amount, price):
"""Place an order on a specific exchange"""
try:
if side == 'buy':
order = await exchange.create_limit_buy_order(symbol, amount, price)
else:
order = await exchange.create_limit_sell_order(symbol, amount, price)
return order
except Exception as e:
print(f"Order placement error on {exchange.id}: {e}")
raise e
Step 4: Monitoring and Adjusting Strategies
Finally, implement systems to monitor performance and continuously improve:
- Build a real-time dashboard to track system performance
- Implement automated alerts for unusual events or errors
- Create performance metrics to evaluate strategy effectiveness
- Develop A/B testing framework to compare strategy variations
- Set up periodic model retraining to adapt to changing market conditions
Case Study: Successful AI Arbitrage Implementation
To illustrate the potential of AI cryptocurrency arbitrage trading, let’s examine a fictional but realistic case study based on common market patterns:

TradeTech AI: Cross-Exchange Arbitrage System
Alex, an experienced algorithmic trader, developed an AI-powered arbitrage system focusing on BTC, ETH, and top 10 altcoins across Binance, Coinbase, and Kraken.
System Architecture:
- Data collection via websocket connections to all three exchanges
- LSTM neural networks for price movement prediction
- Random Forest models for slippage estimation
- Asynchronous execution engine for concurrent trading
- AWS infrastructure with servers in Tokyo, Frankfurt, and Virginia (near exchange data centers)
Performance Metrics (30-Day Period):
- Total opportunities identified: ~12,000
- Opportunities meeting profit threshold (after fees): 3,245
- Successfully executed trades: 2,876 (88.6% success rate)
- Average profit per trade: 0.32% (after all fees)
- Largest single trade profit: 1.87%
- Total return on capital: 9.2% (monthly)
Key Success Factors:
Alex’s system excelled due to several AI-specific advantages:
- Predictive execution: The LSTM model could predict which exchange would update prices first, allowing the system to place orders preemptively
- Dynamic fee optimization: AI continuously adjusted trade sizes to maximize profitability based on current fee structures
- Slippage avoidance: The system accurately predicted and avoided situations where order book depth was insufficient
- 24/7 operation: Unlike human traders, the AI never needed rest and could capitalize on overnight opportunities
Challenges Overcome:
The system wasn’t without challenges. Alex had to solve several problems:
- API rate limiting required sophisticated request management
- Exchange outages necessitated robust error handling
- Market volatility during major news events required dynamic risk adjustment
- Initial overfitting of ML models needed careful cross-validation
Performance Comparison: AI vs. Traditional Approaches
| Metric | Manual Trading | Basic Algorithmic | AI-Powered |
| Opportunities Identified (Daily) | 5-10 | 50-100 | 300-500 |
| Execution Success Rate | 30-40% | 60-70% | 85-95% |
| Average Profit per Trade | 0.5-1.0% | 0.2-0.4% | 0.3-0.5% |
| Monthly Return Potential | 1-3% | 3-6% | 8-15% |
| Risk Management Effectiveness | Low | Medium | High |
| Adaptability to Market Changes | Slow | Limited | Continuous |
Risks and Mitigations in AI Cryptocurrency Arbitrage
While AI cryptocurrency arbitrage trading can be profitable, it comes with significant risks that must be carefully managed:
Market Risks
- Liquidity issues: Price may move significantly when executing larger orders
- Volatility spikes: Sudden market movements can eliminate arbitrage opportunities before execution
- Flash crashes: Extreme price movements can trigger stop losses or cause execution at unfavorable prices
Mitigations:
- Implement dynamic position sizing based on available liquidity
- Use AI to predict and avoid high-volatility periods
- Set maximum drawdown limits and circuit breakers
Technical Risks
- Exchange downtime: API outages can leave positions unhedged
- Latency issues: Slow connections can result in missed opportunities
- API rate limiting: Exchanges may restrict request frequency
Mitigations:
- Implement robust error handling and fallback mechanisms
- Use co-located servers to minimize latency
- Develop sophisticated request management to stay within rate limits
Regulatory Risks
- Changing regulations: New rules may restrict arbitrage activities
- KYC/AML requirements: Withdrawal limits may affect capital movement
- Tax implications: Complex reporting requirements for high-frequency trading
Mitigations:
- Stay informed about regulatory developments in relevant jurisdictions
- Maintain detailed transaction records for compliance
- Consult with legal and tax professionals specializing in cryptocurrency
Exchange-Specific Considerations
Different exchanges present unique challenges for arbitrage trading:
| Exchange | Advantages | Challenges | API Reliability |
| Binance | High liquidity, low fees, extensive API | Strict API rate limits, occasional overloads during high volatility | High (99.5%+) |
| Coinbase Pro | Regulatory compliance, USD pairs, reliable infrastructure | Higher fees, fewer trading pairs, stricter API limits | Very High (99.8%+) |
| Kraken | Fiat support, security focus, European presence | Occasional downtime during peak periods, higher latency | Medium-High (98%+) |
| KuCoin | Many altcoins, competitive fees, good API documentation | Lower liquidity for some pairs, withdrawal delays | Medium (97%+) |
| Bybit | Derivatives focus, low fees, high performance | Fewer spot trading pairs, regulatory uncertainty | High (99%+) |
Protect Your Arbitrage Strategy
Download our comprehensive risk management checklist for AI cryptocurrency arbitrage trading. Includes technical safeguards, market risk controls, and regulatory compliance guidelines.
Future Trends in AI Cryptocurrency Arbitrage
The landscape of AI cryptocurrency arbitrage trading continues to evolve rapidly. Here are the key trends shaping its future:

DeFi Arbitrage Opportunities
Decentralized finance (DeFi) is creating entirely new categories of arbitrage opportunities:
- Cross-protocol arbitrage: Exploiting price differences between different DeFi platforms (Uniswap vs. SushiSwap)
- Flash loan arbitrage: Using uncollateralized loans to execute arbitrage without capital
- Yield farming optimization: AI-driven reallocation of assets to maximize yield
- Cross-chain arbitrage: Exploiting price differences across different blockchains
AI is particularly well-suited to navigate the complexity of DeFi, where opportunities may involve multiple protocols, tokens, and blockchains.
Advanced AI Techniques
Next-generation AI approaches are enhancing arbitrage strategies:
Reinforcement Learning
RL allows trading systems to learn optimal strategies through trial and error:
- Self-improving execution algorithms that adapt to changing market conditions
- Dynamic fee optimization based on exchange conditions
- Automated discovery of complex arbitrage paths
Federated Learning
This approach enables collaborative model training without sharing sensitive data:
- Trading firms can collectively train more powerful models
- Improved prediction accuracy without revealing proprietary strategies
- Reduced data collection requirements for individual traders
Regulatory Evolution
The regulatory landscape for cryptocurrency trading continues to develop:
- Increased scrutiny of high-frequency trading in crypto markets
- Potential reporting requirements for automated trading systems
- Cross-border regulatory frameworks affecting international arbitrage
- KYC/AML enforcement impacting capital movement between exchanges
Successful arbitrage traders will need to stay informed about regulatory developments and ensure their systems remain compliant.
Democratization of AI Trading
Access to sophisticated AI trading tools is becoming more widespread:
- No-code AI platforms allowing non-technical traders to implement arbitrage strategies
- Cloud-based infrastructure reducing the need for expensive hardware
- Open-source AI models providing foundation for custom trading systems
- API-as-a-service providers simplifying exchange connectivity
This democratization is likely to increase competition in arbitrage markets but also drive innovation in strategy development.
Conclusion: Getting Started with AI Cryptocurrency Arbitrage
AI cryptocurrency arbitrage trading represents a powerful approach to generating consistent returns in the volatile crypto market. By leveraging advanced algorithms to identify and execute on price discrepancies across exchanges, traders can capitalize on inefficiencies that would be impossible to exploit manually.

Key Takeaways
- AI provides critical advantages in speed, analysis capacity, and execution precision
- Successful implementation requires technical expertise, quality data, and robust infrastructure
- Risk management is essential to navigate market, technical, and regulatory challenges
- The field continues to evolve with new opportunities in DeFi and advanced AI techniques
- Getting started is increasingly accessible with modern tools and platforms
Whether you’re building a custom system from scratch or leveraging existing tools, the key to success lies in continuous learning, adaptation, and rigorous testing. As markets evolve and new technologies emerge, the most successful arbitrage traders will be those who can quickly incorporate innovations into their strategies while maintaining disciplined risk management.
Ready to Start Your AI Arbitrage Journey?
Get our complete starter kit including code templates, exchange connection guides, and strategy blueprints. Everything you need to build your first AI cryptocurrency arbitrage trading system.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is AI cryptocurrency arbitrage trading legal?
Yes, AI cryptocurrency arbitrage trading is legal in most jurisdictions. Arbitrage is a legitimate trading strategy that helps improve market efficiency by reducing price discrepancies. However, traders should be aware of regulatory requirements in their specific locations, particularly regarding automated trading, tax reporting, and KYC/AML compliance. Some countries may have restrictions on cryptocurrency trading in general, which would also apply to arbitrage activities.
How much capital do I need to start with AI arbitrage?
The capital requirements for effective AI cryptocurrency arbitrage trading vary based on your strategy and target exchanges. While you can technically start with a few hundred dollars, most successful arbitrage operations require at least ,000-,000 to generate meaningful returns after accounting for fees and to overcome minimum order size requirements on exchanges. Larger capital bases (0,000+) allow for more opportunities and better risk distribution. Remember that you’ll also need to allocate funds across multiple exchanges simultaneously.
Do I need programming skills to implement AI arbitrage?
While programming skills are beneficial for building custom AI arbitrage systems, they’re not strictly necessary. Several options exist for traders without coding expertise:
- Use existing arbitrage platforms with built-in AI capabilities
- Leverage no-code AI tools that provide visual interfaces for strategy development
- Partner with technical co-founders or hire developers to implement your strategy
- Start with template code that requires minimal customization
That said, having at least basic Python knowledge will significantly expand your options and allow you to customize strategies to your specific needs.
How do I handle cryptocurrency transfers between exchanges?
Cross-exchange arbitrage often requires transferring cryptocurrencies between platforms, which introduces additional considerations:
- Transfer times: Blockchain confirmation times can range from seconds to hours depending on the network
- Network fees: Transfer costs can significantly impact profitability, especially for smaller trades
- Alternative approach: Many arbitrageurs maintain separate capital pools on each exchange to avoid transfers altogether
For time-sensitive arbitrage, the most efficient approach is typically to maintain balances on all target exchanges rather than transferring funds between them for each opportunity.
What are the tax implications of AI arbitrage trading?
AI cryptocurrency arbitrage trading can create complex tax situations due to the high frequency of transactions and cross-exchange activity. In most jurisdictions, each trade (buy or sell) is a taxable event that must be reported. This can result in significant record-keeping requirements. Additionally, the tax treatment of cryptocurrency varies by country, with some classifying it as property, currency, or commodities.
It’s highly recommended to work with a tax professional experienced in cryptocurrency trading to ensure proper compliance and to implement appropriate tracking systems from the start. Many specialized crypto tax software solutions can help manage the reporting burden.

No comments yet