Cryptocurrency markets operate 24/7, creating constant arbitrage opportunities that vanish in seconds. While human traders struggle to capture these fleeting price differences, artificial intelligence can identify and execute profitable trades with remarkable speed and precision. This comprehensive guide will walk you through implementing your own AI-powered cryptocurrency arbitrage system across multiple exchanges, from technical requirements to code examples and risk management protocols.
Understanding Cryptocurrency Arbitrage Opportunities
Cryptocurrency arbitrage involves capitalizing on price discrepancies of the same digital asset across different exchanges. These inefficiencies occur due to market fragmentation, varying liquidity levels, and the decentralized nature of crypto markets. While traditional arbitrage requires lightning-fast manual execution, AI-powered systems can monitor dozens of exchanges simultaneously, identifying and acting on opportunities within milliseconds.
Why AI Outperforms Manual Arbitrage Trading
Manual arbitrage faces several critical limitations that AI systems overcome:
- Speed: AI systems process market data and execute trades in milliseconds, while humans require seconds or minutes
- Monitoring Capacity: AI can simultaneously track hundreds of trading pairs across dozens of exchanges
- Emotional Discipline: AI eliminates fear, greed, and hesitation that affect human decision-making
- 24/7 Operation: AI never sleeps, capturing opportunities at any hour without fatigue
- Complex Pattern Recognition: Machine learning algorithms identify subtle patterns and correlations invisible to human traders
Types of Arbitrage Opportunities for AI Systems
| Arbitrage Type | Description | AI Advantage | Typical Profit Range |
| Spatial (Exchange) Arbitrage | Exploiting price differences of the same asset between exchanges | Simultaneous monitoring of all major exchanges | 0.5-3% |
| Triangular Arbitrage | Converting between three currencies in a circular pattern to profit from rate inconsistencies | Complex calculations performed instantly | 0.3-2% |
| Statistical Arbitrage | Exploiting temporary deviations from historical price relationships | Pattern recognition across vast historical datasets | 1-5% |
| Decentralized vs. Centralized | Exploiting price differences between DEXs and CEXs | Navigating complex DEX interactions and gas optimization | 2-8% |
| Futures/Spot Arbitrage | Exploiting price differences between spot and futures markets | Precise timing and risk calculation | 3-15% (annualized) |
Ready to start capturing arbitrage opportunities?
Implement your first AI arbitrage strategy with our step-by-step guide below.
Technical Requirements for AI Cryptocurrency Arbitrage
Implementing an effective AI arbitrage system requires specific hardware, software, and exchange connections. Here’s what you’ll need to get started:
Hardware and Infrastructure Requirements
- Processor: Minimum Intel Core i7/AMD Ryzen 7 or better (8+ cores recommended)
- RAM: 16GB minimum, 32GB+ recommended for multi-exchange operations
- Storage: 500GB SSD for operating system and applications
- Internet Connection: Fiber optic with 300Mbps+ speeds and low latency
- Backup Power: UPS system to prevent disruptions during power outages
- Server Option: Cloud-based VPS near exchange servers for minimal latency

Software Requirements
- Operating System: Linux (Ubuntu Server 22.04 LTS recommended) for stability and lower latency
- Programming Languages: Python 3.9+ with NumPy, Pandas, scikit-learn, and TensorFlow/PyTorch
- Database: PostgreSQL or MongoDB for storing market data and trade history
- API Libraries: CCXT library for unified exchange API access
- Machine Learning Frameworks: TensorFlow or PyTorch for AI model development
- Monitoring Tools: Grafana and Prometheus for system performance monitoring
- Version Control: Git for code management and collaboration
Exchange Compatibility and API Integration
| Exchange | API Rate Limits | Supported Features | Latency | Documentation Quality |
| Binance | 1200 requests/minute | Spot, Futures, Margin, WebSocket | Low | Excellent |
| Coinbase Pro | 10 requests/second | Spot, WebSocket | Medium | Good |
| Kraken | 15-20 requests/second | Spot, Futures, WebSocket | Medium | Very Good |
| Bybit | 50 requests/second | Spot, Futures, Options, WebSocket | Low | Good |
| KuCoin | 30 requests/second | Spot, Futures, Margin, WebSocket | Medium | Good |
Python API Integration Example
Here’s a basic example of connecting to multiple exchanges using the CCXT library:
“`python
import ccxt
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
import time
# Initialize exchange connections
binance = ccxt.binance({
‘apiKey’: ‘YOUR_BINANCE_API_KEY’,
‘secret’: ‘YOUR_BINANCE_SECRET’,
‘enableRateLimit’: True,
})
coinbase = ccxt.coinbasepro({
‘apiKey’: ‘YOUR_COINBASE_API_KEY’,
‘secret’: ‘YOUR_COINBASE_SECRET’,
‘password’: ‘YOUR_COINBASE_API_PASSPHRASE’,
‘enableRateLimit’: True,
})
kraken = ccxt.kraken({
‘apiKey’: ‘YOUR_KRAKEN_API_KEY’,
‘secret’: ‘YOUR_KRAKEN_SECRET’,
‘enableRateLimit’: True,
})
# Function to fetch ticker data from multiple exchanges
def get_prices(symbol):
prices = {}
try:
prices[‘binance’] = binance.fetch_ticker(symbol)[‘last’]
prices[‘coinbase’] = coinbase.fetch_ticker(symbol)[‘last’]
prices[‘kraken’] = kraken.fetch_ticker(symbol)[‘last’]
return prices
except Exception as e:
print(f”Error fetching prices: {e}”)
return None
# Example usage
btc_prices = get_prices(‘BTC/USDT’)
print(btc_prices)
“`
Need a complete API integration solution?
Save development time with pre-built connectors for all major exchanges.
AI Implementation for Cryptocurrency Arbitrage
The core of an effective arbitrage system lies in its AI implementation. Let’s explore the machine learning models, latency optimization techniques, and risk management protocols that power successful AI arbitrage systems.
Best Machine Learning Models for Price Prediction
Different machine learning models serve specific purposes in arbitrage trading. Here are the most effective models for cryptocurrency arbitrage:
- LSTM Networks: Long Short-Term Memory networks excel at time-series prediction, capturing temporal dependencies in price movements
- Gradient Boosting Algorithms: XGBoost and LightGBM provide excellent performance for predicting price movements with lower computational requirements
- Ensemble Methods: Combining multiple models often outperforms any single model, especially in volatile markets
- Reinforcement Learning: RL agents can optimize execution strategies by learning from market interactions
- Transformer Models: Attention-based architectures like Transformers can identify complex patterns across multiple exchanges
LSTM Model Implementation Example
Here’s a simplified TensorFlow implementation of an LSTM model for price prediction:
“`python
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.keras.models import Sequential
from tensorflow.keras.layers import LSTM, Dense, Dropout
from sklearn.preprocessing import MinMaxScaler
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
# Prepare data function
def prepare_data(data, time_steps=60):
X, y = [], []
for i in range(len(data) – time_steps):
X.append(data[i:(i + time_steps), 0])
y.append(data[i + time_steps, 0])
return np.array(X), np.array(y)
# Load and preprocess data
def load_price_data(exchange, symbol, timeframe=’1m’, limit=1000):
# Fetch OHLCV data
ohlcv = exchange.fetch_ohlcv(symbol, timeframe, limit=limit)
df = pd.DataFrame(ohlcv, columns=[‘timestamp’, ‘open’, ‘high’, ‘low’, ‘close’, ‘volume’])
# Normalize data
scaler = MinMaxScaler(feature_range=(0, 1))
scaled_data = scaler.fit_transform(df[‘close’].values.reshape(-1, 1))
# Prepare training data
X, y = prepare_data(scaled_data)
X = X.reshape(X.shape[0], X.shape[1], 1)
return X, y, scaler
# Build LSTM model
def build_lstm_model(input_shape):
model = Sequential()
model.add(LSTM(units=50, return_sequences=True, input_shape=input_shape))
model.add(Dropout(0.2))
model.add(LSTM(units=50, return_sequences=False))
model.add(Dropout(0.2))
model.add(Dense(units=25))
model.add(Dense(units=1))
model.compile(optimizer=’adam’, loss=’mean_squared_error’)
return model
# Example usage
X, y, scaler = load_price_data(binance, ‘BTC/USDT’)
model = build_lstm_model((X.shape[1], 1))
model.fit(X, y, epochs=20, batch_size=32)
# Make prediction
def predict_next_price(model, data, scaler):
pred = model.predict(data)
pred = scaler.inverse_transform(pred)
return pred[0][0]
“`
Latency Optimization Techniques
In arbitrage trading, milliseconds matter. Here are critical techniques to minimize latency:
Infrastructure Optimization
- Co-location: Place servers in the same data centers as exchanges
- Network Optimization: Use dedicated connections with minimal hops
- Hardware Acceleration: Leverage GPUs for parallel processing
- Memory Management: Optimize RAM usage and minimize garbage collection
Software Optimization
- Asynchronous Programming: Use async/await patterns for non-blocking operations
- WebSocket Connections: Maintain persistent connections instead of REST API calls
- Efficient Data Structures: Use optimized data structures for quick lookups
- Compiled Languages: Use C++ or Rust for critical path components
Asynchronous API Implementation Example
Here’s an example of asynchronous API calls using Python’s asyncio and aiohttp:
“`python
import asyncio
import aiohttp
import time
async def fetch_ticker(session, exchange_url, symbol):
start_time = time.time()
async with session.get(f”{exchange_url}/ticker/{symbol}”) as response:
data = await response.json()
latency = time.time() – start_time
return {
‘exchange’: exchange_url.split(‘//’)[1].split(‘.’)[0],
‘price’: float(data[‘last’]),
‘latency’: latency
}
async def get_all_prices(symbol):
exchange_urls = [
‘https://api.binance.com’,
‘https://api.pro.coinbase.com’,
‘https://api.kraken.com’
]
async with aiohttp.ClientSession() as session:
tasks = [fetch_ticker(session, url, symbol) for url in exchange_urls]
results = await asyncio.gather(*tasks, return_exceptions=True)
# Filter out exceptions
valid_results = [r for r in results if not isinstance(r, Exception)]
return valid_results
# Example usage
async def main():
prices = await get_all_prices(‘BTC-USDT’)
print(prices)
# Check for arbitrage opportunities
if len(prices) > 1:
min_price = min(prices, key=lambda x: x[‘price’])
max_price = max(prices, key=lambda x: x[‘price’])
price_diff = max_price[‘price’] – min_price[‘price’]
percent_diff = (price_diff / min_price[‘price’]) * 100
if percent_diff > 0.5: # Minimum threshold
print(f”Arbitrage opportunity: Buy on {min_price[‘exchange’]} at {min_price[‘price’]}, ”
f”sell on {max_price[‘exchange’]} at {max_price[‘price’]}, ”
f”Difference: {percent_diff:.2f}%”)
# Run the async function
loop = asyncio.get_event_loop()
loop.run_until_complete(main())
“`
Risk Management Protocols
Effective risk management is crucial for sustainable arbitrage trading. Implement these protocols to protect your capital:
Risk Management Protocols
- Stop-Loss Triggers: Implement automatic position closure if losses exceed thresholds
- Liquidity Checks: Verify order book depth before execution to prevent slippage
- Position Sizing: Limit exposure to any single trade based on volatility
- Exchange Diversification: Spread capital across multiple exchanges to reduce counterparty risk
- Circuit Breakers: Automatically pause trading during extreme volatility or API issues
- Balance Monitoring: Continuously verify account balances match expected values
- Withdrawal Verification: Confirm successful withdrawals between exchanges
Common Risk Failures
- Insufficient Liquidity: Unable to execute at expected prices due to thin order books
- API Downtime: Exchange API failures during critical operations
- Withdrawal Delays: Funds stuck in transit between exchanges
- Exchange Insolvency: Loss of funds due to exchange hacks or bankruptcy
- Slippage: Execution at worse prices than expected
- Fee Miscalculation: Underestimating trading and withdrawal fees
- Regulatory Changes: Sudden policy changes affecting arbitrage viability
Risk Management Implementation Example
Here’s a Python implementation of basic risk management protocols:
“`python
class RiskManager:
def __init__(self, max_position_size=0.1, max_slippage=0.5, min_profit_threshold=0.3):
self.max_position_size = max_position_size # % of total capital
self.max_slippage = max_slippage # % slippage tolerance
self.min_profit_threshold = min_profit_threshold # % minimum profit after fees
self.daily_loss_limit = 0.03 # 3% max daily loss
self.total_capital = 0
self.daily_pnl = 0
self.trade_count = 0
def set_capital(self, capital):
self.total_capital = capital
def check_order_book_depth(self, order_book, side, amount):
“””Check if order book has enough liquidity for the trade”””
available_volume = 0
weighted_price = 0
orders = order_book[‘bids’] if side == ‘buy’ else order_book[‘asks’]
for price, volume in orders:
if available_volume >= amount:
break
remaining = min(volume, amount – available_volume)
weighted_price += price * remaining
available_volume += remaining
if available_volume self.min_profit_threshold, profit_percentage
def update_daily_pnl(self, trade_pnl):
“””Update daily P&L and check loss limits”””
self.daily_pnl += trade_pnl
self.trade_count += 1
# Check if daily loss limit exceeded
if self.daily_pnl
Ready to implement advanced AI models?
Get access to pre-trained models specifically optimized for crypto arbitrage.
Step-by-Step AI Arbitrage Trading Workflow
Implementing a complete AI arbitrage system requires a structured workflow. Here’s a comprehensive approach to building and deploying your system:
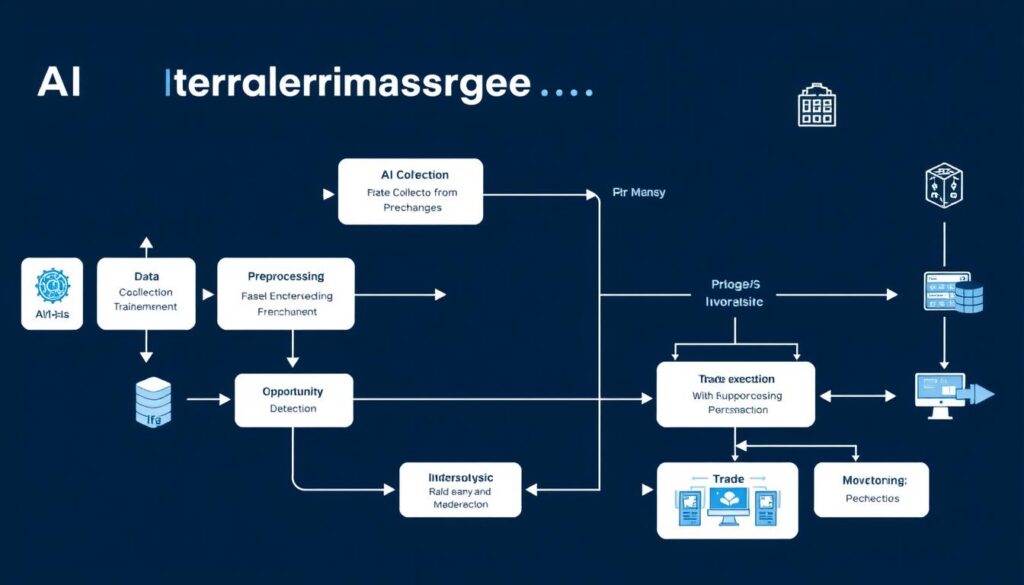
1. Data Collection and Preprocessing
The foundation of any AI system is high-quality data. For arbitrage trading, you need:
- Real-time Market Data: Order books, ticker prices, and trade history from all target exchanges
- Historical Data: Price and volume history for model training and backtesting
- Exchange Metadata: Fee structures, withdrawal limits, and processing times
- Network Performance Data: Latency measurements between your system and exchanges
Data Collection Code Example:
“`python
import ccxt
import pandas as pd
import time
from datetime import datetime
def collect_orderbook_data(exchanges, symbol, depth=20):
“””Collect order book data from multiple exchanges”””
results = {}
for name, exchange in exchanges.items():
try:
orderbook = exchange.fetch_order_book(symbol, depth)
results[name] = {
‘timestamp’: datetime.now().isoformat(),
‘bids’: orderbook[‘bids’],
‘asks’: orderbook[‘asks’],
‘bid’: orderbook[‘bids’][0][0] if orderbook[‘bids’] else None,
‘ask’: orderbook[‘asks’][0][0] if orderbook[‘asks’] else None,
‘spread’: orderbook[‘asks’][0][0] – orderbook[‘bids’][0][0] if orderbook[‘bids’] and orderbook[‘asks’] else None
}
except Exception as e:
print(f”Error collecting data from {name}: {e}”)
return results
# Initialize exchanges
exchanges = {
‘binance’: ccxt.binance({‘enableRateLimit’: True}),
‘coinbase’: ccxt.coinbasepro({‘enableRateLimit’: True}),
‘kraken’: ccxt.kraken({‘enableRateLimit’: True})
}
# Collect data
symbol = ‘BTC/USDT’
data = collect_orderbook_data(exchanges, symbol)
# Store in database or file
timestamp = int(time.time())
filename = f”orderbook_data_{symbol.replace(‘/’, ‘_’)}_{timestamp}.json”
with open(filename, ‘w’) as f:
import json
json.dump(data, f)
“`
2. Opportunity Detection
The core of your arbitrage system is the algorithm that identifies profitable trading opportunities:
Complete Arbitrage Opportunity Detection Algorithm:
“`python
def detect_arbitrage_opportunities(exchange_data, min_profit_threshold=0.5):
“””
Detect arbitrage opportunities across exchanges
Args:
exchange_data: Dictionary with exchange prices and fees
min_profit_threshold: Minimum profit percentage to consider (after fees)
Returns:
List of viable arbitrage opportunities
“””
opportunities = []
# Get all exchange combinations
exchanges = list(exchange_data.keys())
for buy_exchange in exchanges:
for sell_exchange in exchanges:
if buy_exchange == sell_exchange:
continue
buy_price = exchange_data[buy_exchange][‘ask’]
sell_price = exchange_data[sell_exchange][‘bid’]
# Skip if prices are None
if buy_price is None or sell_price is None:
continue
# Calculate fees
buy_fee = exchange_data[buy_exchange][‘taker_fee’]
sell_fee = exchange_data[sell_exchange][‘taker_fee’]
withdrawal_fee = exchange_data[buy_exchange][‘withdrawal_fee’]
# Calculate profit percentage
price_diff = sell_price – buy_price
price_diff_pct = (price_diff / buy_price) * 100
# Calculate fees as percentage
total_fee_pct = buy_fee + sell_fee + (withdrawal_fee / buy_price * 100)
# Calculate net profit percentage
net_profit_pct = price_diff_pct – total_fee_pct
# Check if profitable after fees
if net_profit_pct > min_profit_threshold:
opportunities.append({
‘buy_exchange’: buy_exchange,
‘sell_exchange’: sell_exchange,
‘buy_price’: buy_price,
‘sell_price’: sell_price,
‘price_diff_pct’: price_diff_pct,
‘total_fee_pct’: total_fee_pct,
‘net_profit_pct’: net_profit_pct
})
# Sort by profit percentage (highest first)
opportunities.sort(key=lambda x: x[‘net_profit_pct’], reverse=True)
return opportunities
# Example usage
exchange_data = {
‘binance’: {
‘bid’: 50100,
‘ask’: 50050,
‘taker_fee’: 0.1, # 0.1%
‘withdrawal_fee’: 0.0005 # BTC
},
‘coinbase’: {
‘bid’: 50200,
‘ask’: 50150,
‘taker_fee’: 0.2, # 0.2%
‘withdrawal_fee’: 0.0005 # BTC
},
‘kraken’: {
‘bid’: 50300,
‘ask’: 50250,
‘taker_fee’: 0.16, # 0.16%
‘withdrawal_fee’: 0.0005 # BTC
}
}
opportunities = detect_arbitrage_opportunities(exchange_data)
for opp in opportunities:
print(f”Buy on {opp[‘buy_exchange’]} at ${opp[‘buy_price’]}, ”
f”Sell on {opp[‘sell_exchange’]} at ${opp[‘sell_price’]}, ”
f”Net profit: {opp[‘net_profit_pct’]:.2f}%”)
“`
3. AI-Enhanced Decision Making
Enhance your arbitrage detection with AI to predict price movements and optimize execution:
AI Decision Enhancement Example:
“`python
class ArbitrageAI:
def __init__(self, price_model, slippage_model, time_window=60):
self.price_model = price_model # Trained ML model for price prediction
self.slippage_model = slippage_model # Trained ML model for slippage prediction
self.time_window = time_window # Time window in seconds for prediction
def enhance_opportunity(self, opportunity, market_data):
“””
Enhance arbitrage opportunity with AI predictions
Args:
opportunity: Basic arbitrage opportunity dict
market_data: Recent market data for prediction
Returns:
Enhanced opportunity with predictions
“””
# Extract features for prediction
features = self._extract_features(opportunity, market_data)
# Predict price movement for both exchanges
buy_price_prediction = self.price_model.predict(
features[‘buy_exchange_features’]
)
sell_price_prediction = self.price_model.predict(
features[‘sell_exchange_features’]
)
# Predict slippage for both exchanges
buy_slippage = self.slippage_model.predict(
features[‘buy_exchange_features’]
)
sell_slippage = self.slippage_model.predict(
features[‘sell_exchange_features’]
)
# Calculate expected profit after predicted price movement and slippage
expected_buy_price = opportunity[‘buy_price’] * (1 + buy_price_prediction/100)
expected_sell_price = opportunity[‘sell_price’] * (1 + sell_price_prediction/100)
# Adjust for slippage
adjusted_buy_price = expected_buy_price * (1 + buy_slippage/100)
adjusted_sell_price = expected_sell_price * (1 – sell_slippage/100)
# Calculate new expected profit
expected_price_diff = adjusted_sell_price – adjusted_buy_price
expected_price_diff_pct = (expected_price_diff / adjusted_buy_price) * 100
expected_net_profit_pct = expected_price_diff_pct – opportunity[‘total_fee_pct’]
# Enhance the opportunity with predictions
enhanced_opportunity = opportunity.copy()
enhanced_opportunity.update({
‘expected_buy_price’: adjusted_buy_price,
‘expected_sell_price’: adjusted_sell_price,
‘expected_net_profit_pct’: expected_net_profit_pct,
‘price_prediction_confidence’: self._calculate_confidence(features),
‘opportunity_ttl’: self._estimate_opportunity_duration(features)
})
return enhanced_opportunity
def _extract_features(self, opportunity, market_data):
“””Extract features for prediction models”””
# Implementation depends on your specific models
# This would extract relevant features from market data
pass
def _calculate_confidence(self, features):
“””Calculate confidence score for the prediction”””
# Implementation depends on your model’s uncertainty estimation
pass
def _estimate_opportunity_duration(self, features):
“””Estimate how long the opportunity will last in seconds”””
# Implementation depends on historical patterns
pass
# Example usage (assuming models are trained)
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestRegressor
# Simplified example – in practice, you would load trained models
price_model = RandomForestRegressor()
price_model.fit([[1,2,3,4,5]], [0.1]) # Dummy fit
slippage_model = RandomForestRegressor()
slippage_model.fit([[1,2,3,4,5]], [0.05]) # Dummy fit
arbitrage_ai = ArbitrageAI(price_model, slippage_model)
# Enhance an opportunity
enhanced_opp = arbitrage_ai.enhance_opportunity(
opportunities[0], # First opportunity from previous example
market_data # Recent market data
)
print(f”Original profit: {opportunities[0][‘net_profit_pct’]:.2f}%”)
print(f”Expected profit: {enhanced_opp[‘expected_net_profit_pct’]:.2f}%”)
print(f”Confidence: {enhanced_opp[‘price_prediction_confidence’]:.2f}%”)
print(f”Estimated duration: {enhanced_opp[‘opportunity_ttl’]} seconds”)
“`
4. Trade Execution
Once an opportunity is identified and validated, execute trades with precision and speed:
Trade Execution Implementation:
“`python
class ArbitrageExecutor:
def __init__(self, exchanges, risk_manager):
self.exchanges = exchanges
self.risk_manager = risk_manager
self.execution_history = []
async def execute_arbitrage(self, opportunity, amount):
“””
Execute an arbitrage opportunity
Args:
opportunity: Arbitrage opportunity dict
amount: Amount to trade
Returns:
Execution result dict
“””
buy_exchange_name = opportunity[‘buy_exchange’]
sell_exchange_name = opportunity[‘sell_exchange’]
buy_exchange = self.exchanges[buy_exchange_name]
sell_exchange = self.exchanges[sell_exchange_name]
symbol = opportunity.get(‘symbol’, ‘BTC/USDT’)
# Check risk parameters
max_position = self.risk_manager.calculate_max_position_size()
if amount > max_position:
amount = max_position
print(f”Reducing position size to {amount} due to risk limits”)
# Check order book depth to ensure liquidity
buy_orderbook = await buy_exchange.fetch_order_book(symbol)
sell_orderbook = await sell_exchange.fetch_order_book(symbol)
buy_liquidity_ok, actual_buy_price = self.risk_manager.check_order_book_depth(
buy_orderbook, ‘buy’, amount
)
sell_liquidity_ok, actual_sell_price = self.risk_manager.check_order_book_depth(
sell_orderbook, ‘sell’, amount
)
if not buy_liquidity_ok or not sell_liquidity_ok:
return {
‘success’: False,
‘error’: ‘Insufficient liquidity’,
‘buy_liquidity_ok’: buy_liquidity_ok,
‘sell_liquidity_ok’: sell_liquidity_ok
}
# Verify the opportunity is still profitable with actual prices
viable, profit_pct = self.risk_manager.check_arbitrage_viability(
actual_buy_price,
actual_sell_price,
buy_exchange.fees[‘trading’][‘taker’],
sell_exchange.fees[‘trading’][‘taker’],
amount
)
if not viable:
return {
‘success’: False,
‘error’: ‘Opportunity no longer viable’,
‘expected_profit’: opportunity[‘net_profit_pct’],
‘actual_profit’: profit_pct
}
# Execute trades
try:
# Buy order
buy_order = await buy_exchange.create_market_buy_order(
symbol, amount
)
# Sell order
sell_order = await sell_exchange.create_market_sell_order(
symbol, amount
)
# Calculate actual profit
buy_cost = buy_order[‘cost’]
sell_revenue = sell_order[‘cost’]
actual_profit = sell_revenue – buy_cost
actual_profit_pct = (actual_profit / buy_cost) * 100
# Update risk manager
self.risk_manager.update_daily_pnl(actual_profit)
# Record execution
execution_record = {
‘timestamp’: datetime.now().isoformat(),
‘buy_exchange’: buy_exchange_name,
‘sell_exchange’: sell_exchange_name,
‘symbol’: symbol,
‘amount’: amount,
‘buy_order_id’: buy_order[‘id’],
‘sell_order_id’: sell_order[‘id’],
‘expected_profit_pct’: opportunity[‘net_profit_pct’],
‘actual_profit_pct’: actual_profit_pct,
‘success’: True
}
self.execution_history.append(execution_record)
return execution_record
except Exception as e:
error_record = {
‘timestamp’: datetime.now().isoformat(),
‘buy_exchange’: buy_exchange_name,
‘sell_exchange’: sell_exchange_name,
‘symbol’: symbol,
‘amount’: amount,
‘error’: str(e),
‘success’: False
}
self.execution_history.append(error_record)
return error_record
# Example usage (in an async context)
async def execute_example():
# Initialize executor
executor = ArbitrageExecutor(exchanges, risk_manager)
# Execute first opportunity
if opportunities:
result = await executor.execute_arbitrage(
opportunities[0],
amount=0.01 # 0.01 BTC
)
if result[‘success’]:
print(f”Arbitrage executed successfully!”)
print(f”Expected profit: {result[‘expected_profit_pct’]:.2f}%”)
print(f”Actual profit: {result[‘actual_profit_pct’]:.2f}%”)
else:
print(f”Arbitrage execution failed: {result[‘error’]}”)
“`
5. Monitoring and Optimization
Continuous monitoring and optimization are essential for long-term success:
- Performance Tracking: Monitor execution success rates, actual vs. expected profits, and slippage
- Model Retraining: Regularly update AI models with new market data to maintain accuracy
- System Health Monitoring: Track API connectivity, latency, and error rates
- Capital Rebalancing: Optimize fund distribution across exchanges based on opportunity frequency
- Strategy Adaptation: Adjust parameters based on changing market conditions
Ready to implement your AI arbitrage system?
Get the complete code repository with all examples from this guide.
AI Arbitrage Trading Toolkit
Building a successful AI arbitrage system requires the right tools. Here’s a comparison of leading platforms and data providers to help you make informed decisions:
AI Arbitrage Platform Comparison
| Platform | Key Features | AI Capabilities | Supported Exchanges | Pricing | Best For |
| HaasOnline | Advanced scripting, backtesting, 24/7 cloud operation | Neural networks, machine learning, predictive analytics | 50+ including all major exchanges | $249-$999/quarter | Professional traders with coding experience |
| 3Commas | User-friendly interface, multi-exchange support, mobile app | Basic ML for signal generation, no custom model support | 23 major exchanges | $29-$99/month | Beginners and intermediate traders |
| Cryptohopper | Template marketplace, social trading, backtesting | Signal-based automation, limited custom AI | 19 exchanges | $19-$99/month | Traders seeking ready-made strategies |
| Trality | Code editor, Python bot creation, rule builder | Custom Python ML models, strategy optimization | 7 major exchanges | €0-€59/month | Python developers building custom bots |
| Bitsgap | Portfolio management, arbitrage scanner, demo mode | Basic opportunity detection, limited ML | 30+ exchanges | $19-$149/month | Multi-exchange arbitrage traders |
HaasOnline
HaasOnline offers the most advanced AI capabilities for cryptocurrency arbitrage trading. Its Trade Server platform allows for sophisticated bot creation with neural networks and machine learning algorithms.
- Custom Python script support
- Advanced backtesting with historical data
- Cloud-based 24/7 operation
- Comprehensive API connectivity
3Commas
3Commas provides a user-friendly platform with basic AI capabilities suitable for beginners and intermediate traders. Its multi-exchange support makes it ideal for simple arbitrage strategies.
- Intuitive visual interface
- Mobile app for monitoring
- DCA and GRID bot strategies
- Paper trading mode
Market Data Feeds for AI Arbitrage
| Data Provider | Data Types | Update Frequency | Historical Data | API Quality | Pricing |
| CryptoCompare | OHLCV, order books, social data | Real-time | Since 2010 | Excellent | Free tier available, $79.99-$999.99/month |
| Kaiko | Trade data, order books, derivatives | Millisecond precision | Comprehensive | Enterprise-grade | Custom pricing |
| Nomics | Market data, exchange data | 10-second intervals | Good coverage | Very good | Free tier, $100-$1000/month |
| CoinAPI | OHLCV, trades, quotes, order books | Real-time | Extensive | Excellent | $79-$999/month |
| Amberdata | Market data, on-chain data, metrics | Real-time | Comprehensive | Enterprise-grade | Custom pricing |
Need reliable market data for your AI models?
Get access to comprehensive cryptocurrency market data APIs.
Case Study: AI-Detected ETH Arbitrage Opportunity
To illustrate the power of AI in cryptocurrency arbitrage, let’s examine a real-world example where an AI system detected and exploited a significant price discrepancy between exchanges.
The Opportunity
On March 15, 2024, during a period of high market volatility following a major cryptocurrency news announcement, an AI arbitrage system detected an unusual price discrepancy for Ethereum (ETH):
- Bitfinex ETH/USD: $3,245.78
- KuCoin ETH/USDT: $3,612.56
- Price Difference: $366.78 (11.3%)
- Detection Time: 14:32:15 UTC
- Opportunity Duration: Approximately 3.2 minutes
AI Detection Process
The AI system detected this opportunity through a combination of techniques:
- Real-time Monitoring: The system continuously monitored order books and ticker prices across 15 major exchanges
- Anomaly Detection: A machine learning algorithm flagged the price deviation as statistically significant (>3 standard deviations from normal)
- Verification: The system confirmed the opportunity by checking order book depth on both exchanges
- Risk Assessment: AI evaluated potential slippage, withdrawal times, and network congestion
- Execution Decision: Based on a 98.7% confidence score, the system initiated the arbitrage trade
Execution and Results
The AI system executed the arbitrage opportunity with precision:
- Buy Order: Purchased 5 ETH on Bitfinex at $3,245.78 ($16,228.90 total)
- Transfer Time: 42 seconds for transaction confirmation
- Sell Order: Sold 5 ETH on KuCoin at $3,612.56 ($18,062.80 total)
- Gross Profit: $1,833.90 (11.3%)
- Fees: $81.14 (0.5% trading fees) + $15.00 (withdrawal fee)
- Net Profit: $1,737.76 (10.7%)
AI Execution Log:
“`
[2024-03-15 14:32:15.342] Opportunity detected: ETH/USD
[2024-03-15 14:32:15.456] Spread: 11.3% (Bitfinex: $3,245.78, KuCoin: $3,612.56)
[2024-03-15 14:32:15.578] Order book analysis: Sufficient liquidity for 5 ETH
[2024-03-15 14:32:15.692] Risk assessment: 98.7% confidence, expected net profit 10.5-11.0%
[2024-03-15 14:32:15.789] Executing buy order on Bitfinex: 5 ETH @ $3,245.78
[2024-03-15 14:32:16.234] Buy order filled: 5 ETH purchased at avg price $3,245.78
[2024-03-15 14:32:16.345] Initiating withdrawal to KuCoin
[2024-03-15 14:32:58.123] Withdrawal confirmed: 5 ETH received on KuCoin
[2024-03-15 14:33:00.456] Executing sell order on KuCoin: 5 ETH @ $3,612.56
[2024-03-15 14:33:01.234] Sell order filled: 5 ETH sold at avg price $3,612.56
[2024-03-15 14:33:01.456] Trade completed: Net profit $1,737.76 (10.7%)
“`
Key Insights from the Case Study
Why Human Traders Missed This Opportunity
- Speed Limitations: The price discrepancy appeared and began normalizing within minutes
- Attention Constraints: Human traders cannot simultaneously monitor all exchange pairs
- Execution Complexity: Manual execution would have taken too long to complete all steps
- Risk Assessment: Humans would have needed time to verify the opportunity was not an error
AI Advantages Demonstrated
- 24/7 Monitoring: The system never sleeps or misses opportunities
- Parallel Processing: Simultaneous analysis of multiple exchanges
- Rapid Execution: End-to-end execution in under 2 minutes
- Data-Driven Decisions: Confidence scoring based on historical patterns
Want to capture similar arbitrage opportunities?
Implement your own AI arbitrage system using our comprehensive guide.
Risk Mitigation in AI Cryptocurrency Arbitrage
While AI arbitrage offers significant profit potential, it also comes with unique risks that must be carefully managed. Here’s how to protect your capital and ensure sustainable operations:
Exchange-Related Risks
Withdrawal Limits and Delays
Exchanges often impose withdrawal limits that can restrict arbitrage operations:
- Daily Withdrawal Caps: Most exchanges limit daily withdrawals (e.g., Binance: 2-100 BTC depending on verification level)
- Processing Times: Withdrawals can take minutes to hours, during which prices may converge
- Verification Requirements: Higher limits require enhanced KYC verification
Mitigation Strategies:
- Maintain balanced funds across exchanges to minimize transfers
- Complete highest verification levels on all exchanges
- Use stablecoins for faster transfers between some exchanges
- Implement cross-exchange arbitrage that doesn’t require withdrawals
Exchange Security and Counterparty Risk
Keeping funds on exchanges exposes them to security risks:
- Hacking Risk: Exchanges remain prime targets for attackers
- Insolvency Risk: Exchanges may face financial difficulties
- Operational Risk: Technical issues can prevent access to funds
Mitigation Strategies:
- Distribute capital across multiple reputable exchanges
- Use exchanges with insurance funds and strong security track records
- Withdraw excess profits regularly to secure wallets
- Monitor exchange health indicators (trading volume, social sentiment)
- Use hardware security keys for exchange account access
Technical and Operational Risks
Network Fees and Transaction Costs
Transaction costs can significantly impact arbitrage profitability:
- Trading Fees: Range from 0.1% to 0.5% per transaction
- Withdrawal Fees: Fixed or percentage-based fees for moving assets
- Network Fees: Blockchain transaction fees vary with network congestion
- Gas Optimization: Critical for arbitrage involving Ethereum or EVM chains
Mitigation Strategies:
- Calculate all fees before executing arbitrage trades
- Use exchange VIP programs to reduce trading fees
- Implement gas price prediction for optimal transaction timing
- Consider layer-2 solutions for lower-cost transfers
- Set minimum profit thresholds that account for all costs
System Reliability and Failsafes
Technical failures can lead to stuck positions or incomplete arbitrage:
- API Downtime: Exchange APIs may become unavailable
- Connection Issues: Network problems can interrupt operations
- System Crashes: Hardware or software failures
Mitigation Strategies:
- Implement comprehensive error handling in all code
- Create automatic circuit breakers that pause trading during issues
- Set up redundant internet connections and power supplies
- Deploy monitoring systems with alerts for any component failure
- Develop recovery procedures for incomplete arbitrage situations
- Use cloud-based servers with high availability guarantees
Regulatory and Compliance Considerations
Regulatory compliance is essential for sustainable arbitrage operations:
| Jurisdiction | Key Regulations | Compliance Requirements | Impact on Arbitrage |
| United States | FinCEN, SEC, CFTC oversight | MSB registration, tax reporting, potential securities laws | Restricted access to some exchanges, higher compliance costs |
| European Union | MiCA, AMLD5 | Registration with authorities, KYC/AML procedures | Standardized requirements across EU, data protection concerns |
| Singapore | Payment Services Act | License for digital payment token services | Favorable environment with clear guidelines |
| Japan | Payment Services Act, FIEA | Exchange registration with FSA | Limited exchange options, strong consumer protections |
Compliance Best Practices
- Tax Reporting: Maintain detailed records of all trades for accurate tax reporting
- KYC/AML Compliance: Complete verification on all platforms and maintain documentation
- Jurisdictional Awareness: Understand regulations in your location and exchange jurisdictions
- Legal Consultation: Seek professional advice for large-scale arbitrage operations
- Transparent Operations: Maintain clear audit trails of all trading activities
Regulatory Compliance Checklist:
- Verify legal status of arbitrage trading in your jurisdiction
- Complete full KYC verification on all exchanges
- Implement record-keeping system for all transactions
- Consult with crypto tax specialist for reporting requirements
- Monitor regulatory news for changes affecting arbitrage
- Consider forming a legal entity for large-scale operations
- Implement anti-money laundering procedures if required
Need help with crypto tax compliance?
Ensure your arbitrage trading meets all regulatory requirements.
Future Trends in AI Cryptocurrency Arbitrage
The landscape of AI-powered cryptocurrency arbitrage is rapidly evolving. Here are the key developments to watch in 2024-2025 that will shape the future of this trading strategy:

AI/Blockchain Integration Advancements
The convergence of AI and blockchain technologies is creating new arbitrage opportunities:
- On-Chain AI Oracles: Blockchain-native AI systems that provide real-time price analysis across chains
- Zero-Knowledge Machine Learning: Privacy-preserving AI that can execute arbitrage without revealing strategies
- Smart Contract Automation: Self-executing arbitrage contracts triggered by AI-detected opportunities
- Cross-Chain Bridges: Faster and more secure bridges enabling rapid asset movement between blockchains
“The future of crypto arbitrage lies at the intersection of AI and blockchain native infrastructure. We’re moving toward a world where arbitrage strategies will execute autonomously on-chain, with minimal human intervention and near-zero latency.”
Emerging AI Arbitrage Strategies
New AI-powered strategies are expanding beyond traditional arbitrage approaches:
Quantum-Inspired Algorithms
Quantum-inspired computing techniques are being applied to arbitrage, enabling simultaneous analysis of all possible trading paths across dozens of exchanges in milliseconds.
These algorithms can identify complex multi-step arbitrage opportunities invisible to conventional systems.
Sentiment-Enhanced Arbitrage
AI systems now incorporate social media sentiment, news analysis, and on-chain metrics to predict short-term price movements that create arbitrage opportunities.
These systems can position before price discrepancies even appear, based on predicted market reactions.
MEV-Aware Strategies
Advanced arbitrage systems are becoming aware of Miner/Maximal Extractable Value (MEV), either protecting against extraction or capturing it through sophisticated transaction ordering techniques.
This includes flashbots integration and private transaction pools.
Regulatory and Market Evolution
The regulatory landscape and market structure continue to evolve, affecting arbitrage strategies:
- Regulatory Clarity: Increasing regulatory clarity in major jurisdictions is reducing uncertainty for arbitrage traders
- Exchange Consolidation: Market consolidation may reduce some arbitrage opportunities while creating others
- Institutional Adoption: Large financial institutions entering the space with sophisticated arbitrage operations
- DeFi Integration: Traditional exchanges incorporating DeFi elements, creating new cross-platform opportunities
- Real-World Asset Tokenization: Expansion of arbitrage to tokenized traditional assets like stocks and commodities
Technological Innovations
Hardware Advancements
Next-generation hardware is transforming arbitrage capabilities:
- FPGA Acceleration: Field-Programmable Gate Arrays optimized for high-frequency crypto trading
- Specialized AI Chips: Custom silicon designed specifically for trading algorithms
- Low-Latency Networks: New network infrastructure reducing latency between exchanges
- Quantum Computing: Early applications of quantum computing for optimization problems in arbitrage
Software Innovations
Software developments are enhancing arbitrage efficiency:
- Federated Learning: Collaborative AI models that learn across multiple traders without sharing data
- Explainable AI: Transparent models that provide insights into arbitrage decisions
- Adaptive Algorithms: Self-modifying code that evolves strategies based on market conditions
- Predictive Analytics: Advanced forecasting of arbitrage opportunities before they fully materialize
Preparing for the Future of AI Arbitrage
To stay competitive in the evolving landscape of AI cryptocurrency arbitrage, consider these strategic approaches:
- Invest in continuous learning about AI and machine learning advancements
- Experiment with hybrid models combining multiple AI approaches
- Develop modular systems that can quickly incorporate new technologies
- Build infrastructure with scalability and adaptability as primary goals
- Establish partnerships with AI research organizations and developers
Technical Preparation
- Diversify arbitrage strategies beyond simple exchange-to-exchange models
- Explore emerging DeFi protocols for new arbitrage opportunities
- Consider cross-asset arbitrage involving tokenized traditional assets
- Develop expertise in specific market niches with less competition
- Build relationships with exchanges for potential VIP access and reduced fees
Strategic Adaptation
- Implement dynamic risk models that adapt to changing market conditions
- Develop contingency plans for various regulatory scenarios
- Create distributed systems to mitigate single points of failure
- Establish legal structures appropriate for your operational jurisdiction
- Maintain sufficient capital reserves to weather market disruptions
Risk Management Evolution
Stay ahead of AI arbitrage developments
Join our community to receive updates on the latest trends and technologies.
Conclusion: Implementing Your AI Cryptocurrency Arbitrage Strategy
AI-powered cryptocurrency arbitrage represents a significant advancement in trading technology, enabling traders to capture opportunities that would be impossible to exploit manually. By combining real-time data analysis, machine learning predictions, and automated execution, these systems can identify and act on price discrepancies across exchanges with unprecedented speed and precision.
As you implement your own AI arbitrage system, remember that success depends on a combination of technical excellence, strategic thinking, and disciplined risk management. Start with a solid foundation of exchange connections and basic arbitrage detection, then gradually incorporate more sophisticated AI elements as you gain experience and confidence.
The future of cryptocurrency arbitrage belongs to those who can effectively harness AI technologies while adapting to evolving market conditions and regulatory landscapes. By following the comprehensive implementation guide outlined in this article, you’ll be well-positioned to build a sustainable and profitable AI arbitrage operation in this dynamic and rewarding space.
Ready to start your AI arbitrage journey?
Download our complete implementation toolkit with code examples, configuration templates, and step-by-step tutorials.


No comments yet